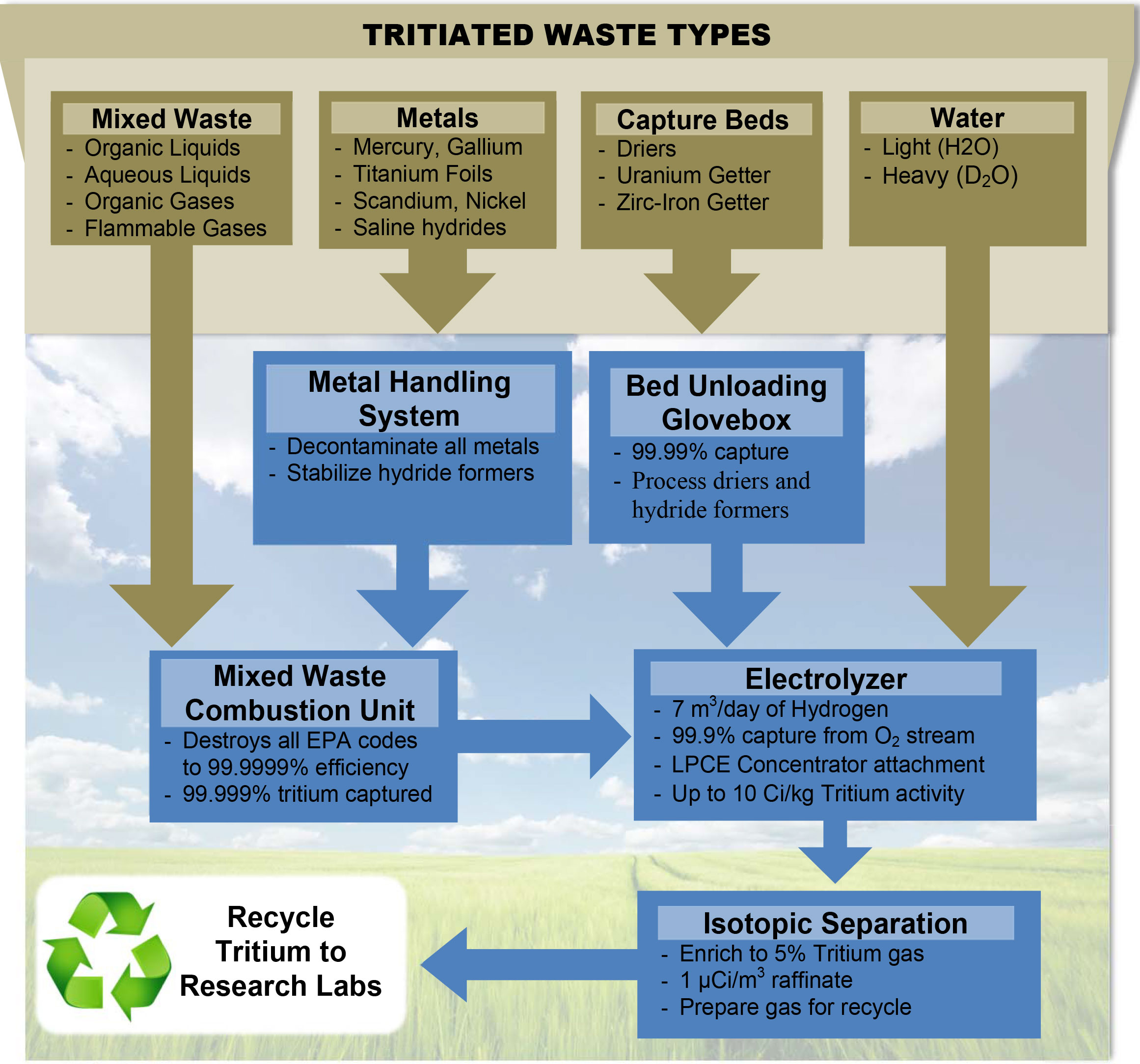
The mixed waste combustion facility (MWCF) is an EPA approved system that destroys all EPA codes in liquid or gas inside a catalytic furnace operating at high temperatures. Once organic compounds have been broken down the resulting tritiated water is captured in the vapor after the furnace. The vapor is condensed in an efficient scrubber and collected as tritiated water. The carrier steam is dried with molecular sieves to remove trace tritiated water vapor. Periodically the driers are regenerated to recover the water as a condensate.
The tritiated water can then be passed to the next phase of the operation, electrolysis.
The electrolysis cell (Ecell) is an alkaline cell that can handle very high activities of tritium. The Ecell breaks water down into hydrogen and oxygen. The tritiated hydrogen is directed to the next step in the process (the LPCE) to reduce the volume of water while the oxygen is cleaned of all elemental and oxide forms of hydrogen and released.
The Ecell is able to process both light water (H2O) and heavy water (D2O).
The Tritium in Metal Station is a high-activity tritium gas handling station which incorporates a boron silicate furnace that can be heated to 900 C. This system drives off and collects tritium gas from uranium beds, titanium foils, and other tritiated metals.
The tritiated gas can either be sent to the MWCF for oxidation into tritiated water or directly to the ISS system for further processing.
The Bed Unloading Station (BUS) is a versatile station installed in a glove box with peripherals that allows for the unloading of tritiated gas or moisture from a variety of capture or storage beds. The glove box can handle most beds that are 24” in height and can supply compressed air, nitrogen, argon, hydrogen or helium gas to unload and condition any type of bed. Typical beds that are processed are: molecular sieve beds, zirc iron beds, copper beds, and nickel beds but all hydride formers can be processed in this facility.
All hydrogen from these devices is oxidized and collected as tritiated water. The tritiated water is then sent to the Ecell for tritium extraction.
The Isotopic Separation System (ISS) is a thermal diffusion tritiated hydrogen gas separation system. The high activity hydrogen gas (HT) from the Ecell is directed into the thermal diffusion chamber. The heavier tritium gas settle to the bottom of the thermal diffusion column while the lighter H2 gas rise to the top. The low activity (< 0.1 µCi/m^3) raffinate is drawn from the top as more HT gas is added. Once the lower gas achieves concentrations up to 5% pure tritium the active product is drawn and stored on a metal hydride getter bed.
The final 5% pure tritium gas product on the getter bed can for enriched further for re-use in the tritium community.
 CSBD Technologies
CSBD Technologies
